Air stripping
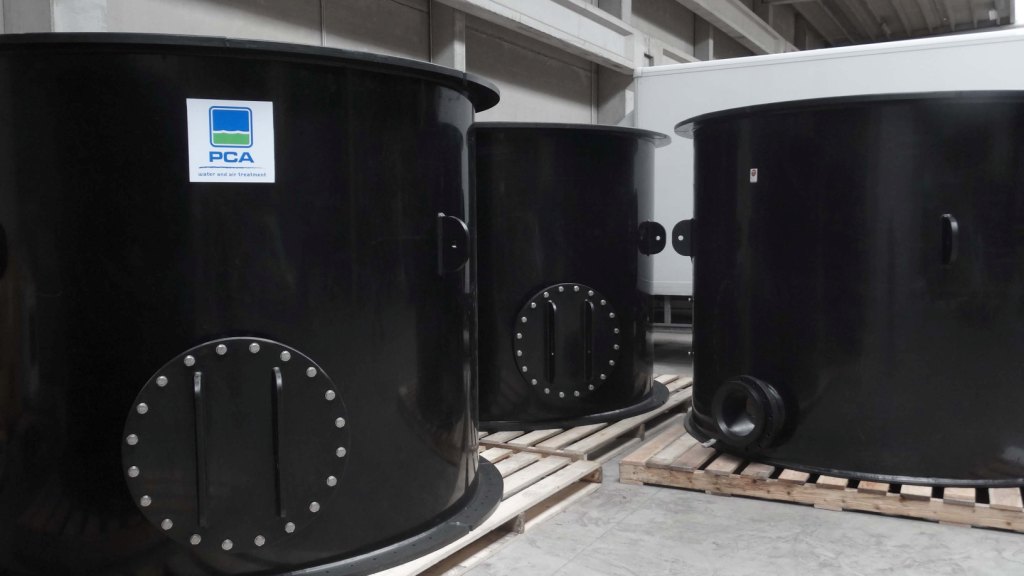
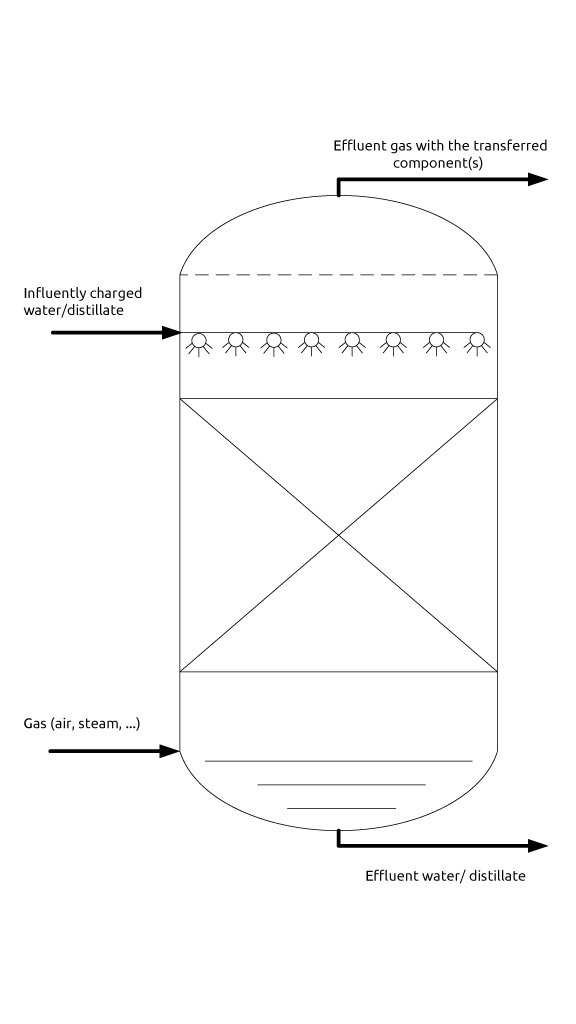
Air strippers are used to clean waste water, digestate or polluted groundwater using air. Through intensive contact between air and water, the volatile compounds present in the waste or ground water are transferred to the air.
The incoming air flow is low in the substances to be removed, so that the substances, due to the difference in concentration between the rich water and the poor air, pass from the water to the gas phase. The speed of this process depends on the difference in concentration between the water phase and the gas phase, the volatility of the substances and the temperature.
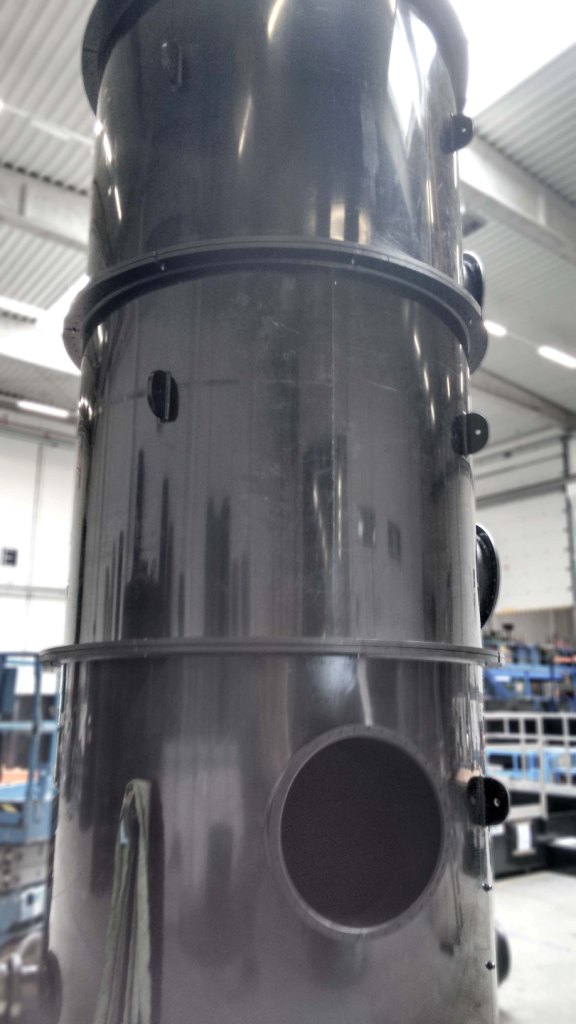
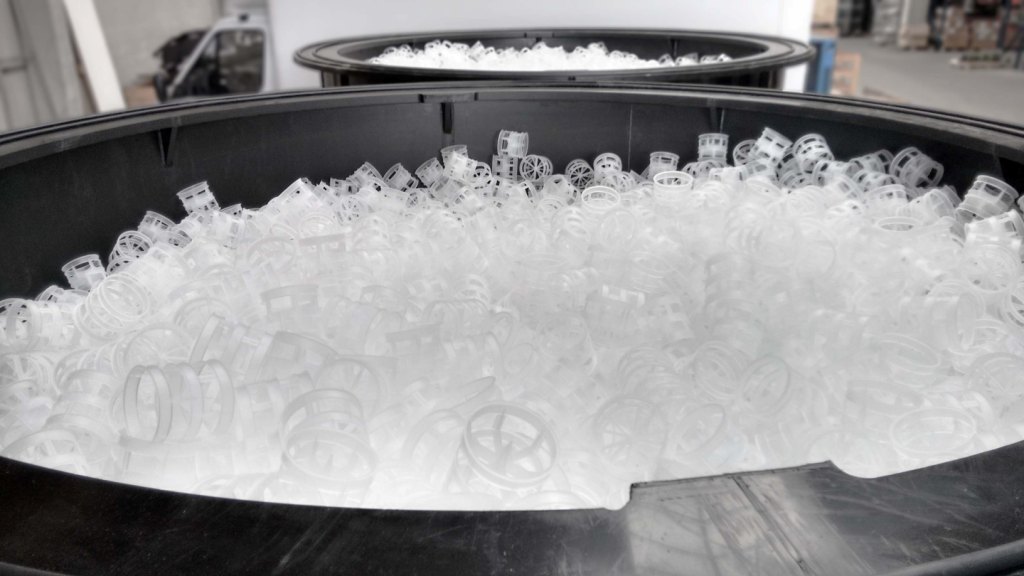
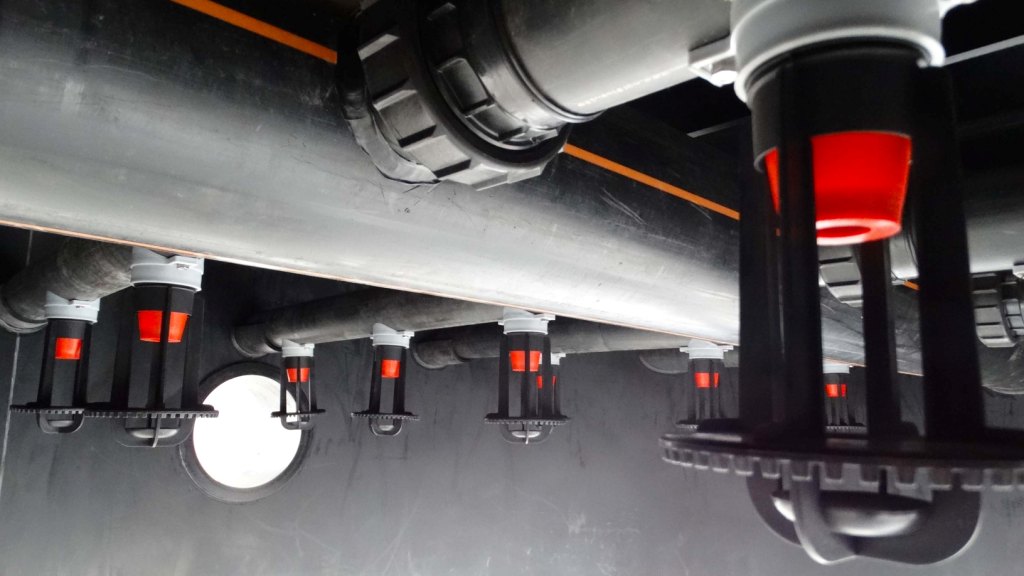
Air stripping is carried out with the aid of a stripping tower or a plate stripper. The stripping tower or stripping column uses counter flow, where a vertically positioned column is filled with packing material. The plate stripper uses cross flow, whereby the water flow is intensively aerated through a perforated plate.
Finally, the same principle is applied to steam stripping, but the air is replaced by steam. In such a process, a highly concentrated stream can be recovered (e.g. NH₃).
| Advantages: | Industries: |
| - Low investment costs | - Waste water treatment |
| - Reliable | - Groundwater treatment |
| - Environmentally beneficial | - Chemical industry |
| - Easy to employ | - Pharmaceutical industry |
| - Wide range of applications | - ... |
| - High efficiency | |
| - Recycling of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC), NH₃, … | |
| Air strippers are used for the removal of: | |
| - Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) like methane (CH₄) | - Sulphur compounds |
| - Ammonia (NH₃) | - Chlorinated solvents |
| - Carbon Disulphide (CS₂) | - ... |